|
|||||||||||||||||
Medieval Gothic Art in Italy
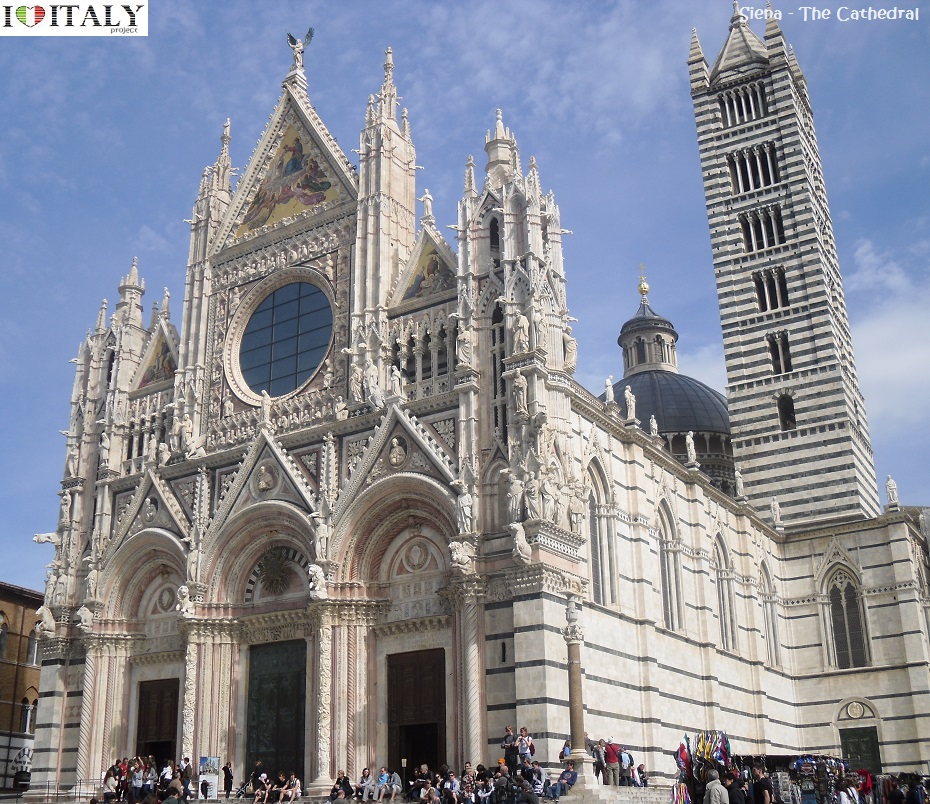
 Italian text by AnnaLisa Limardi - Translation and adaptation by Domenico Russumanno  The passage from Romanesque to Gothic in architecture is marked by the increasing height of buildings, the appearance of the pointed arch, the slimming down of bulk and the growing complexity of ribbing. The passage from Romanesque to Gothic in architecture is marked by the increasing height of buildings, the appearance of the pointed arch, the slimming down of bulk and the growing complexity of ribbing. The characteristic forms that were to define Gothic architecture grew out of Romanesque architecture and developed at several different geographic locations, as the result of different influences and structural requirements. However Italian Gothic had a different character from the rest of Europe: it was less linear, leaving large flat surfaces, and more sensitive to Classical ideas of harmony. Great Gothic churches and cathedral grew up all over Italy. The most famous examples are perhaps in Umbria (basilica of San Francesco in Assisi, Orvieto Cathedral, Saint Croce and Santa Maria del Fiore in Florence) and Venice ( St Zanipolo, Santa Maria dei Frari) but there are also important buildings in Genoa, Naples and Palermo.  Siena Cathedral, the Divine Beauty. Heart of the art, history and tradition of Siena. The Duomo of Siena whose impressive mass rises in the homonymous piazza, constitutes one of the most illustrious examples of Romanesque-Gothic cathedral in Italy. It was was consecrated in 1179 in the presence of pope Alessandro III Bandinelli from Siena, following the peace treaty signed with Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I, known as Barbarossa.
 The basilica of San Francesco in Assisi, which was begun in 1228, is built into the side of a hill and comprises two churches known as the Upper Church and the Lower Church, and a crypt where the remains of the saint are interred.
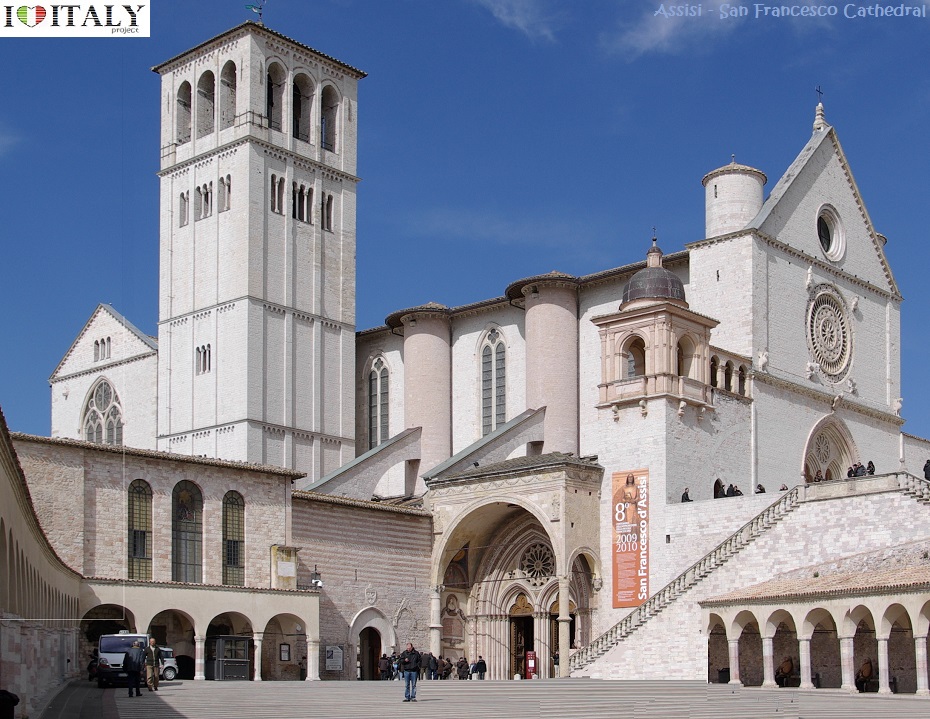 The interior of the Upper Church is an important early example of the Gothic style in Italy.
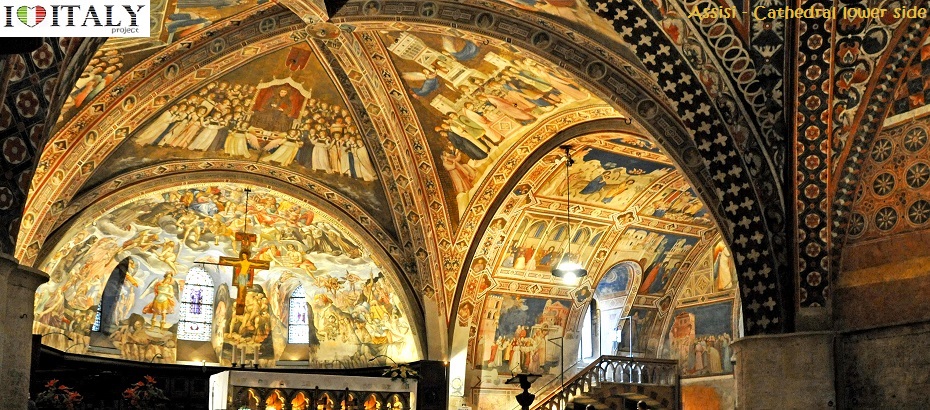 The Upper and Lower Churches are decorated with frescoes by numerous late medieval painters from the Roman and Tuscan schools, and include works by Cimabue, Giotto, Simone Martini, Pietro Lorenzetti and possibly Pietro Cavallini. The range and quality of the works gives the basilica a unique importance in demonstrating the development of Italian art of this period.
 Orvieto Cathedral - Classic piece of religious construction. The cathedral is dedicated to Santa Maria Assunta (Assumption of Mary). Construction began in 1290 and completed in 1591.The Gothic façade is considered to be one of the great masterpieces of the Late Middle Ages.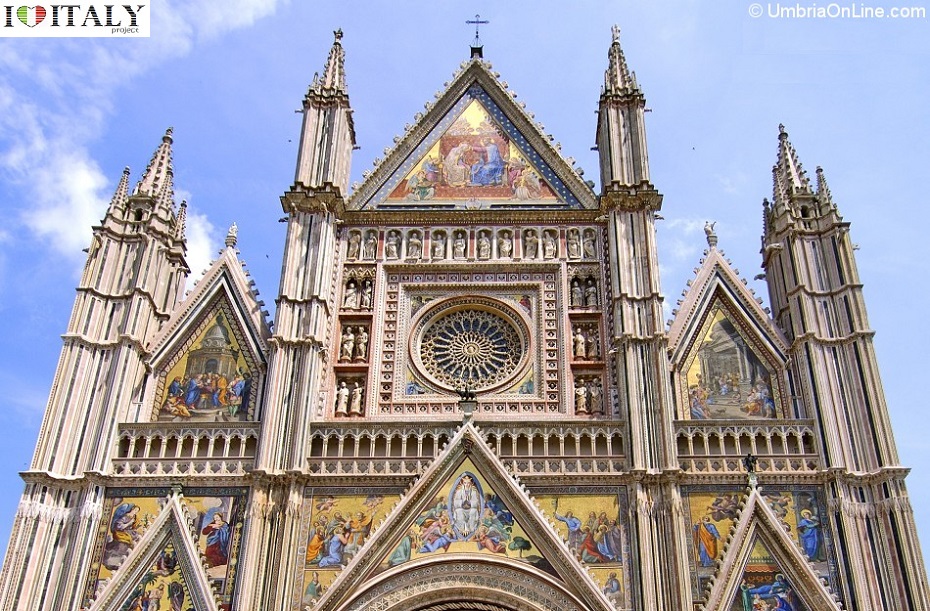  The most exciting and eye-catching part is its golden frontage, which is decorated by large bas-reliefs and statues with the symbols (Angel, Ox, Lion, Eagle) of the Evangelists, standing on the cornice above the sculptured panels on the piers.
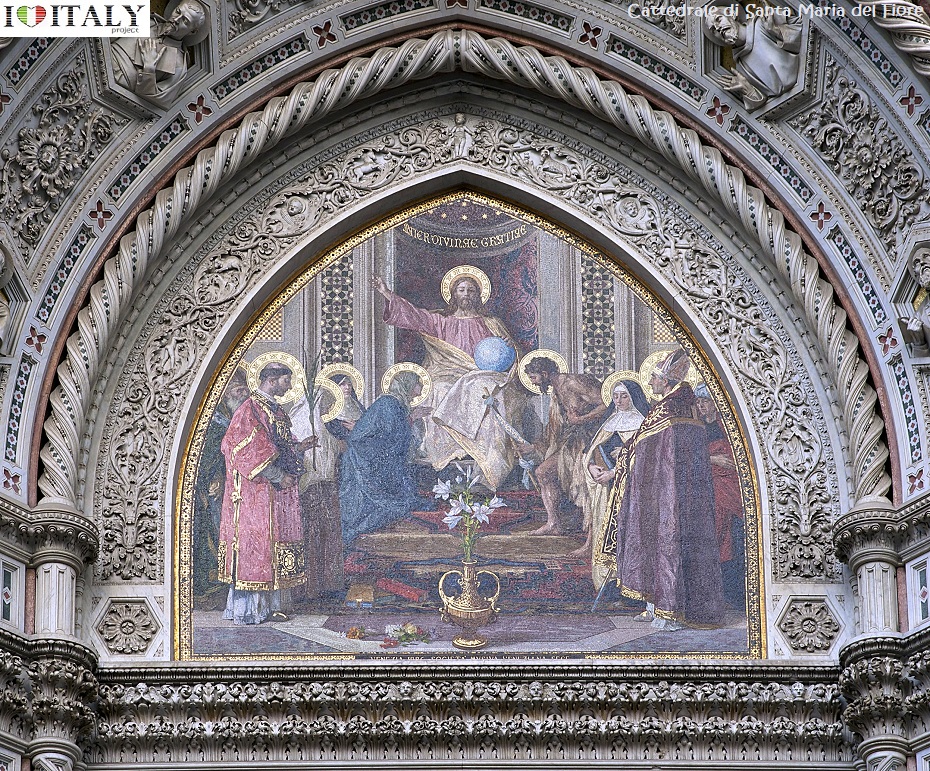
The bas-reliefs on the piers depict biblical stories from the Old and New Testament. They are considered among the most famous of all 14th-century sculpture.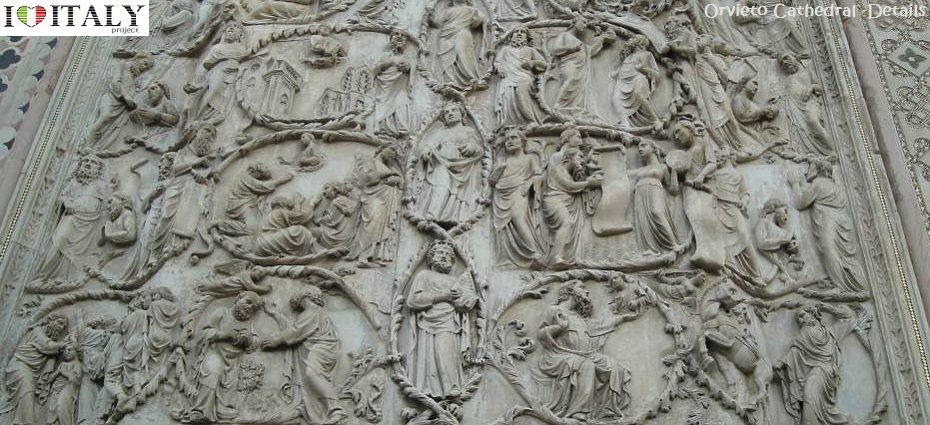  The Basilica di Santa Croce (Basilica of the Holy Cross) is the principal Franciscan church in Florence. It is situated on the Piazza di Santa Croce, less then a km away from the Duomo. It is the burial place of some of the most illustrious Italians, such as Michelangelo, Galileo, Machiavelli, Foscolo, Gentile and Rossini, thus it is known also as the Temple of the Italian Glories (Tempio dell'Itale Glorie). The Basilica is the largest Franciscan church in the world. Its most notable features are its sixteen chapels, many of them decorated with frescoes by Giotto and his pupils, and its tombs and cenotaphs.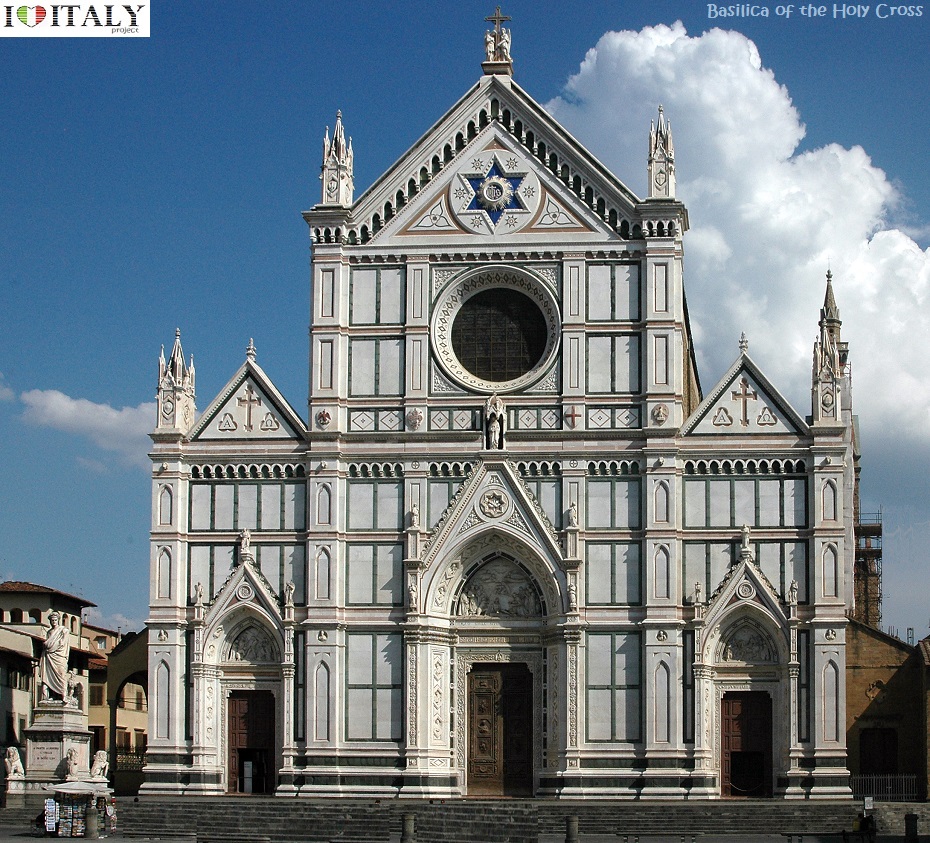  One of the most impressive projects of the Renaissance. "Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower" ( Cattedrale di Santa Maria del Fiore), is Florence's main church and one of Italy's largest. Work started in 1296 on the site of an earlier cathedral dedicated to Saint Reparata, and completed structurally in 1436 . The Gothic style cathedral complex, located in Piazza del Duomo, includes the Baptistery and Giotto's Campanile. The three buildings are part of the UNESCO World Heritage.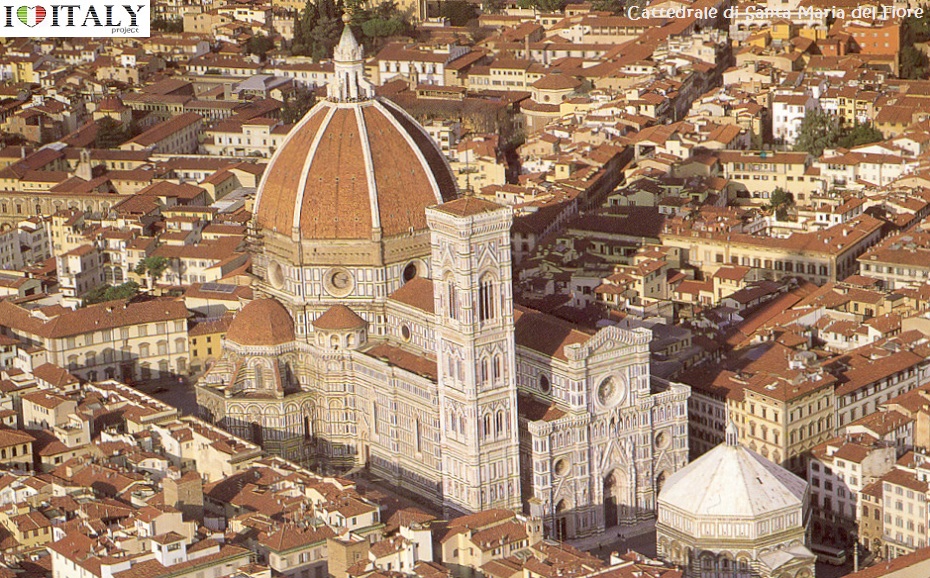  Interior details - Tympanum central mosaic
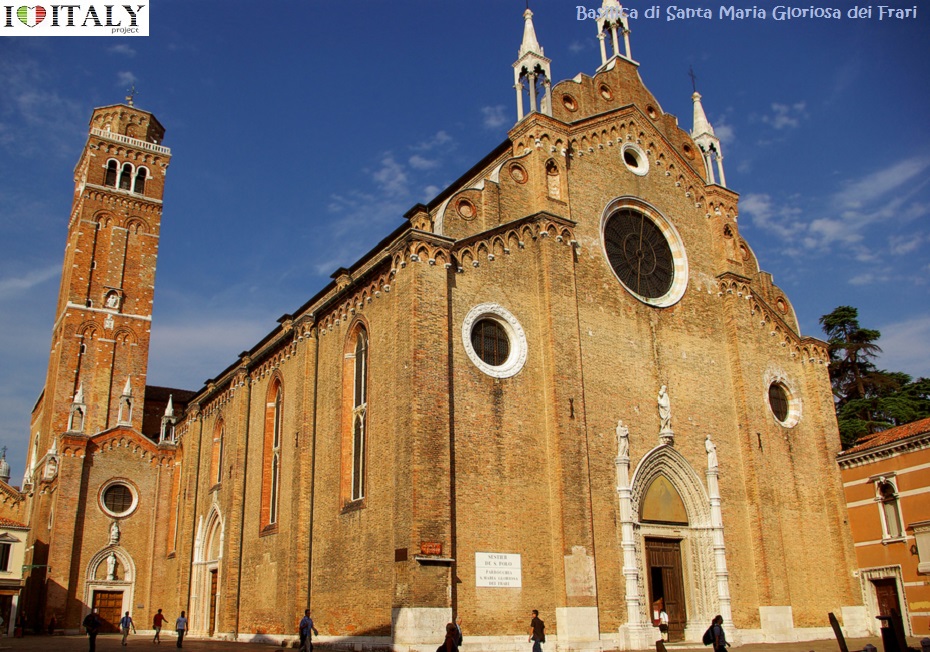
 One of Venezia's largest churches is the Basilica di San Giovanni e Paolo, (known in the Venetian dialect as San Zanipolo) - Work began 1333 with the demolition of a previous church and completed in 1430. The huge brick edifice presents the classic Italian Gothic style and was built to hold large congregations. It is dedicated to John and Paul, not the Biblical Apostles of the same names, but two obscure martyrs of the Early Christian church in Rome, whose names were recorded in the 3rd century but whose legend is of a later date.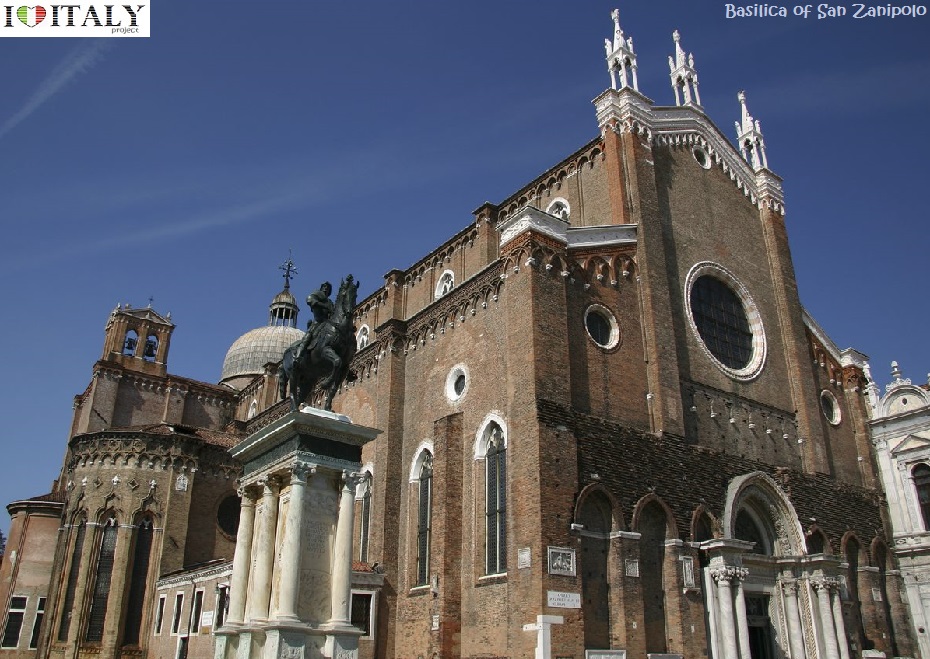  Another great Venezian church is the Basilica di Santa Maria Gloriosa dei Frari, usually just called the Frari. The Franciscans were granted land to build a church in 1250, but the building was not completed until 1338. Work almost immediately began on its much larger replacement, the current church, which took over a century to build. The campanile, the second tallest in the city after that of San Marco, was completed in 1396. It is dedicated to the Assumption (Assunzione della Beata Vergine).
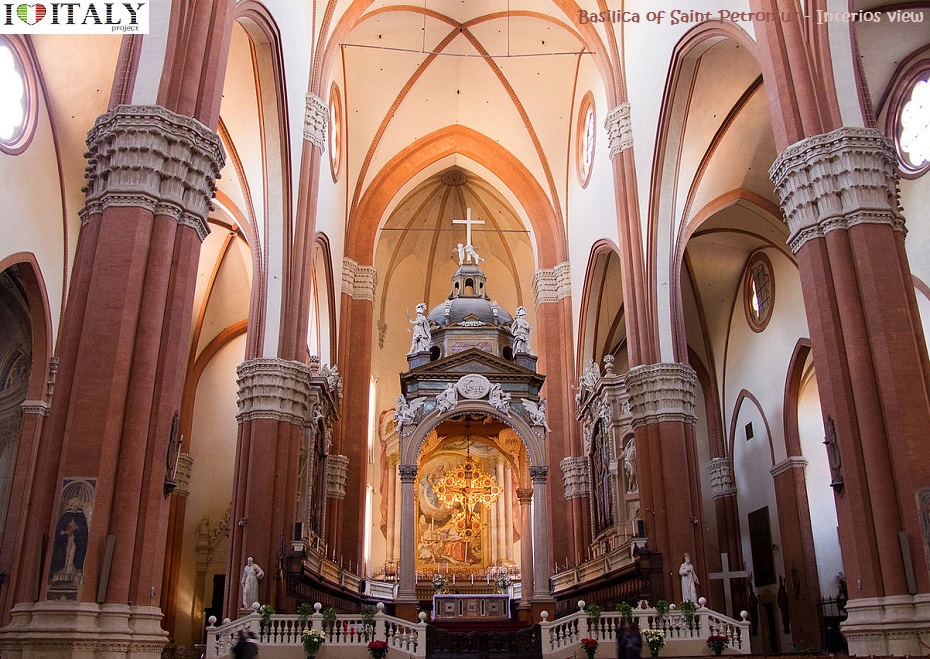
 Altar - Interior details.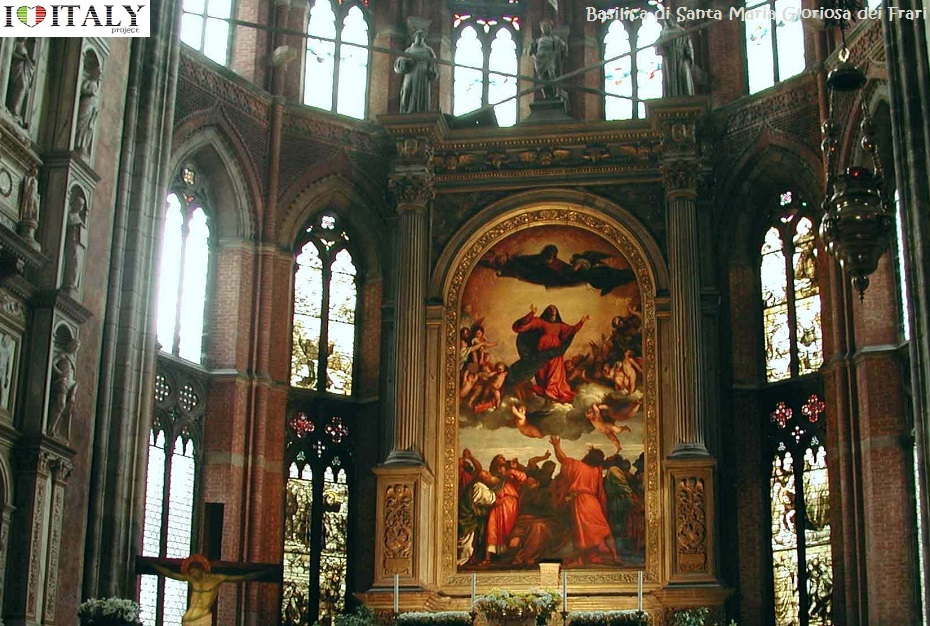  The last great examples of this style, drawing closer to the taste of northern Europe, are the basilica of St Petronio, with three naves, in Bologna and Milan Cathedral with five.
Dominating Bologna's Piazza Maggiore is the Basilica of San Petronio (Saint Petronius), the patron saint of the city. It is the fifteenth largest church in the world, 132 metres long and 66 metres wide, while the vault reaches 45 metres inside and 51 metres in the facade. The first stone of construction was laid June 7, 1390. Works lasted for several centuries. Completed in 1479 after the completion of the first version of the facade, in 1393 the first pair of side chapels were begun. The series were completed only in 1479. However, in 1514 a revised plan was proposed in the form of a Latin cross with the intent to outdo even Saint Peter's Basilica of Rome. According to tradition, Pope Pius IV halted such a majestic project.
The facing of the main facade remains unfinished: many architects were commissioned to propose solutions for it, but a definitive one was never found.
 The interior houses a Madonna with Saints. Also the colours of the walls and a stained glass windows are noteworthy.
 The Duomo di Milano is dedicated to St Mary of the Nativity (Santa Maria Nascente). The Gothic cathedral took nearly six centuries to complete. It is the 5th-largest church in the world and the second largest in Italy. The cathedral occupies what was the most central site in Roman Mediolanum. The first cathedral, the "new basilica" (basilica nova) dedicated to St Thecla, was completed by 355. An adjoining basilica was erected in 836. The old baptistery, the Battistero Paleocristiano, dates to 335 and still can be visited under the Milan Cathedral. When a fire damaged the cathedral and basilica in 1075, they were rebuilt as the Duomo. Construction began in 1386 .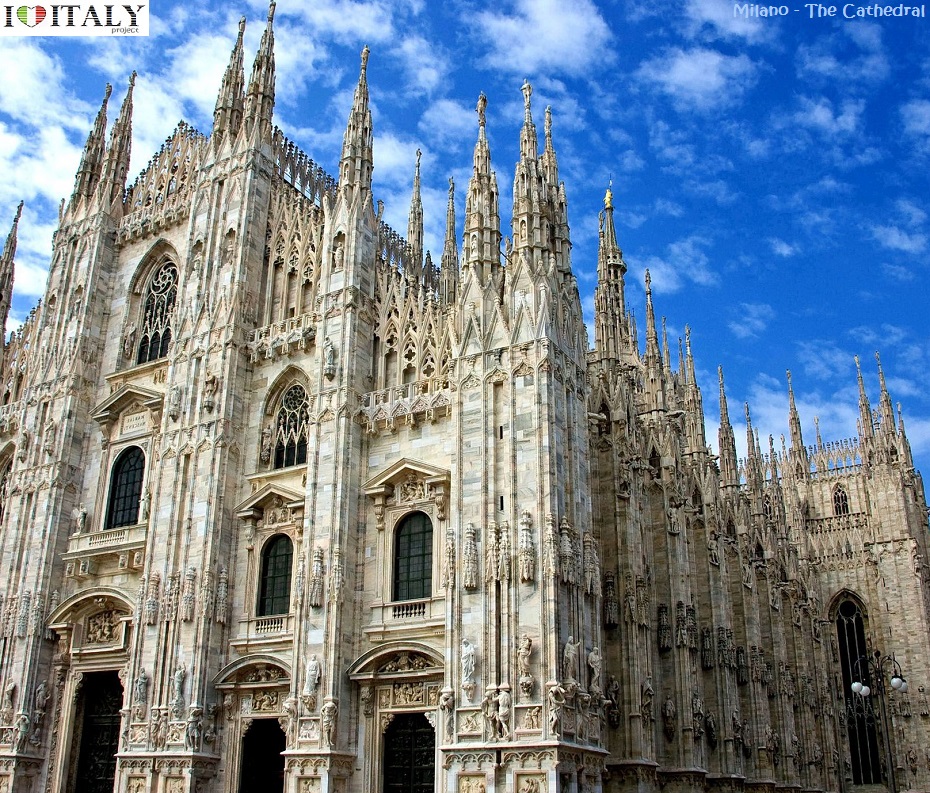  The roof is open to tourists (for a fee), which allows many a close-up view of some spectacular sculpture that would otherwise be unappreciated. The roof of the cathedral is renowned for the forest of openwork pinnacles and spires, set upon delicate flying buttresses.
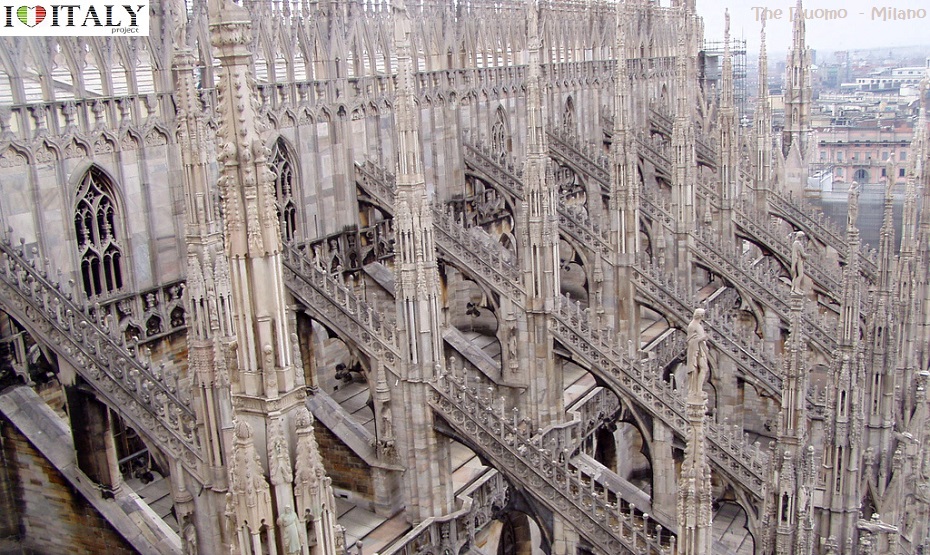 The cathedral's five broad naves, divided by 40 pillars, are reflected in the hierarchic openings of the façade. Even the transepts have aisles.
The nave columns are 24.5 metres (80 ft) high, and the apsidal windows are 20.7 x 8.5 metres (68 x 28 feet). The huge building is of brick construction, faced with marble from the quarries which Gian Galeazzo Visconti donated in perpetuity to the cathedral chapter. Its maintenance and repairs are very complicated.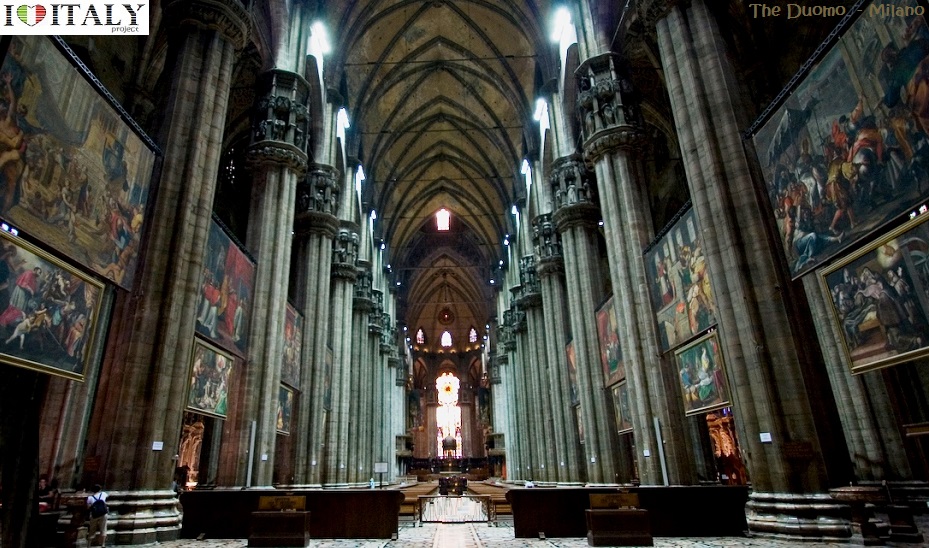   The splendor of the cathedrals contrast with the sobriety of the abbeys which also appeared throughout the peninsula, especially due to the Cistercians. Examples include Chiaravalle Milanese, Chiaravalle della Colomba, Fossanova, Casamari , St. Galgano, St Nicola in Agrigento.
The Abbey of Santa Maria di Rovegnano, Chiaravalle Milanese is a Cistercian monastic complex in the comune of Milan.
An abbey (Catholic or Anglican monastery or convent) are typically under the authority of an Abbot or an Abbess, serving as the spiritual father or mother of the community. In fact very often for abbey in place names it is meant not only the building itself, as well as the settlement that developed around it. The hamlet borgo that has developed round the abbey was once an independent commune called Chiaravalle Milanese, now included in Milan and referred to as the Chiaravalle district.
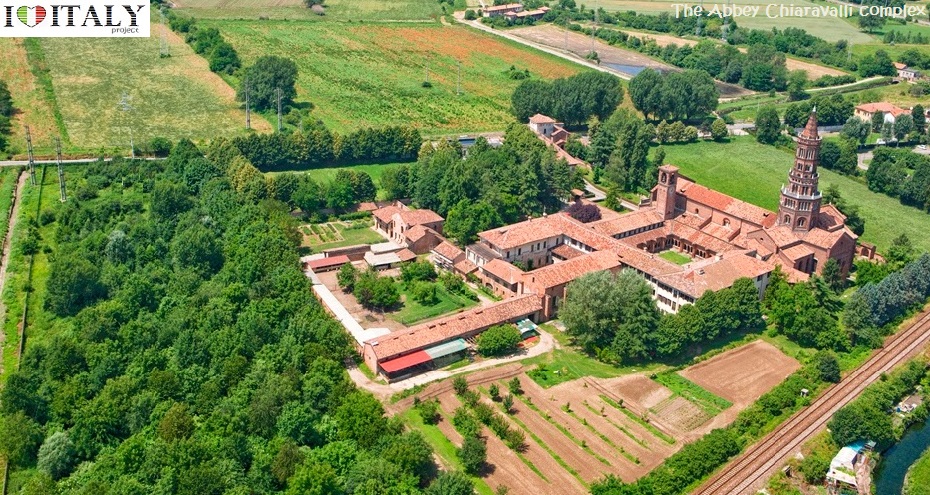 The abbey was founded on 22 January 1135 as a daughterhouse of Clairvaux; it is one of the first examples of Gothic architecture in Italy, although maintaining some late Romanesque influences.
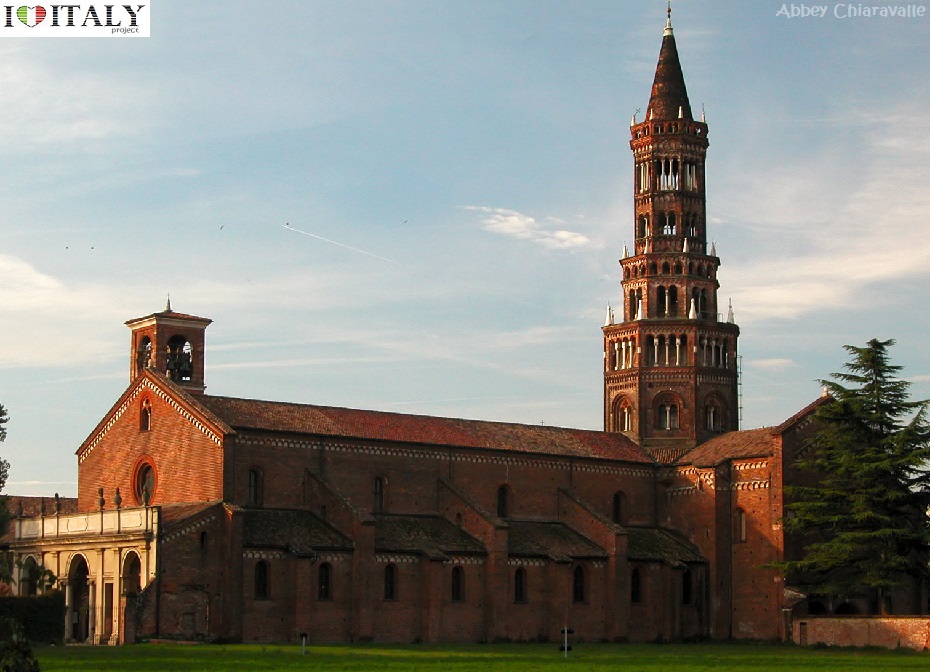 The abbey of Chiaravalle della Colomba is a Cistercian abbey founded in April 11, 1136 and is situated at Alseno (Piacenza) in the region of Emilia Romagna.
 Glimpse of the interior.
 The Fossanova Abbey, is located about 100 Km from Rome near Priverno in the province of Latina. It still retains the bare architecture, the magnificent rose window and the finely carved capitals, reflecting the prominent role within the area.
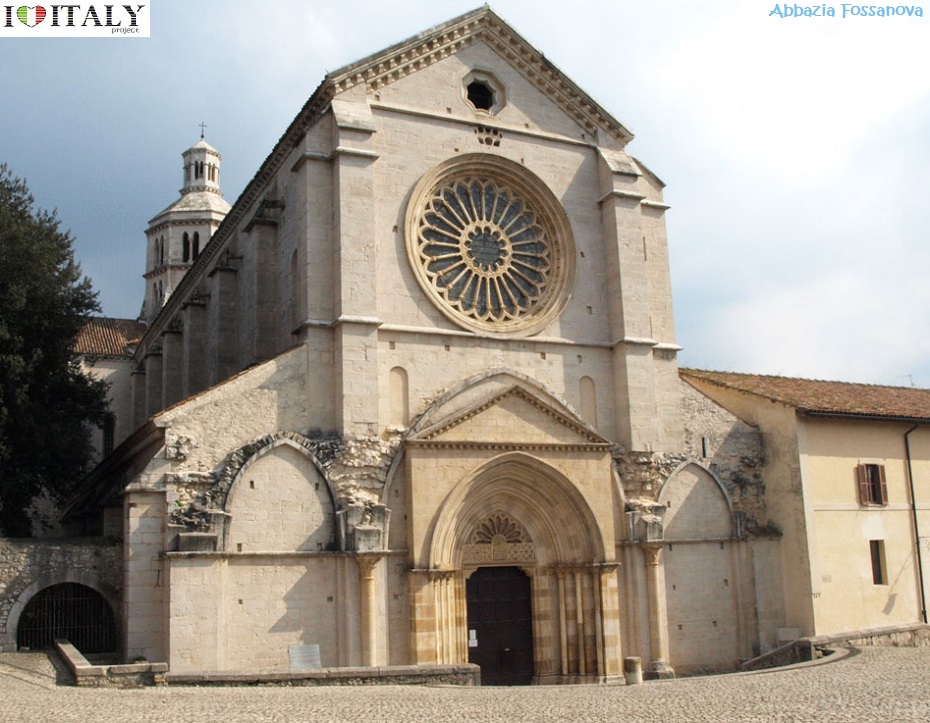 This Cistercian abbey is one of the finest examples of the Burgundian Early Gothic style in Italy, dated from around 1135.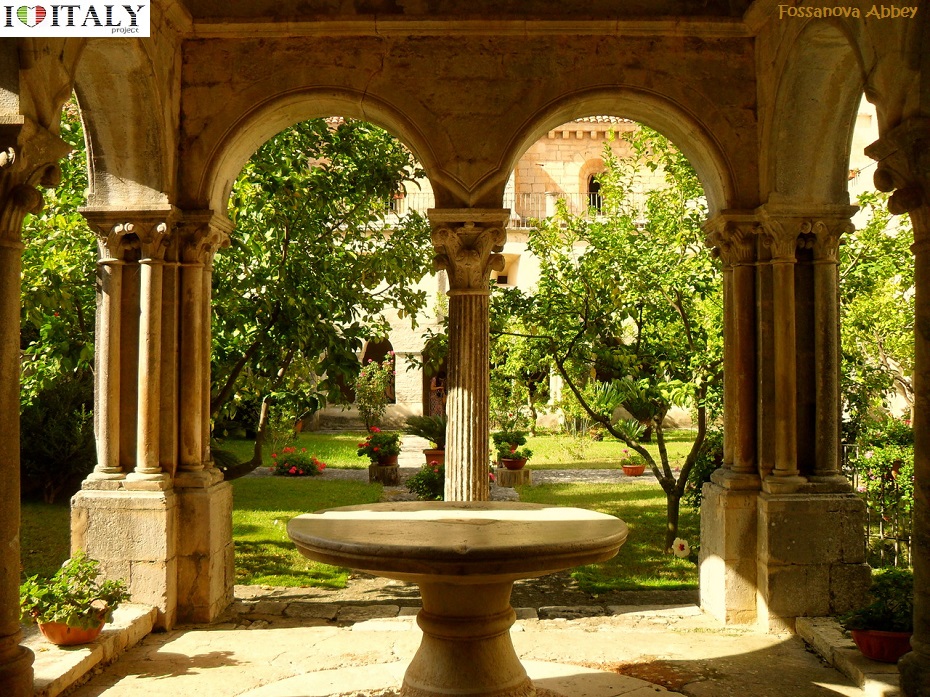  The abbey of Casamari is situated in the territory of Veroli (Frosinone), on the Via Maria, mid-way between Frosinone and Sora. It was built on the ruins of an ancient Roman municipium named Cereatae, being dedicated to the goddess Ceres.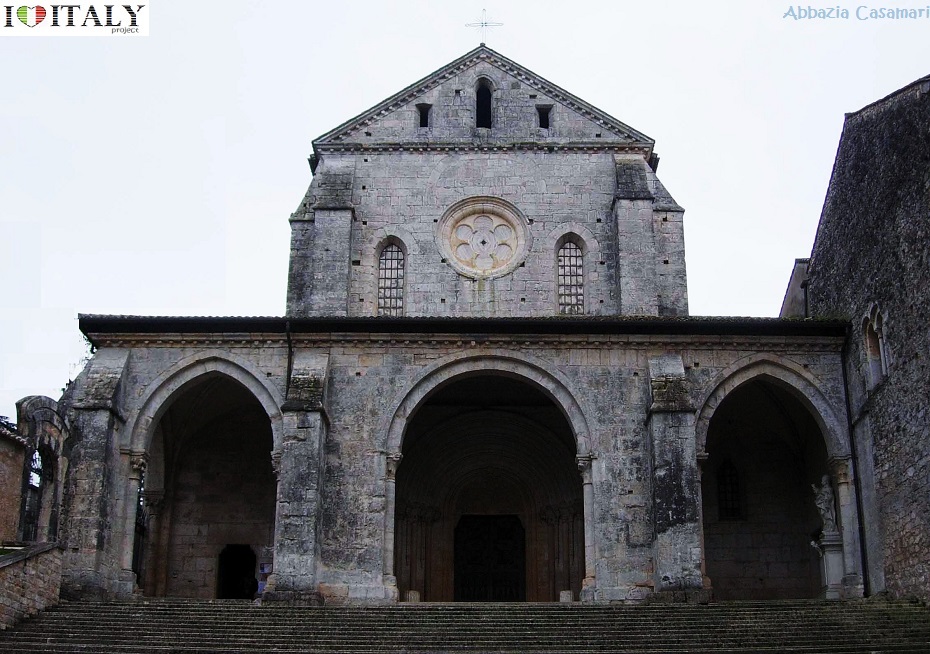  Documents witness the presence of a Benedectine monastic community in the 11th century, under the name of Casamari.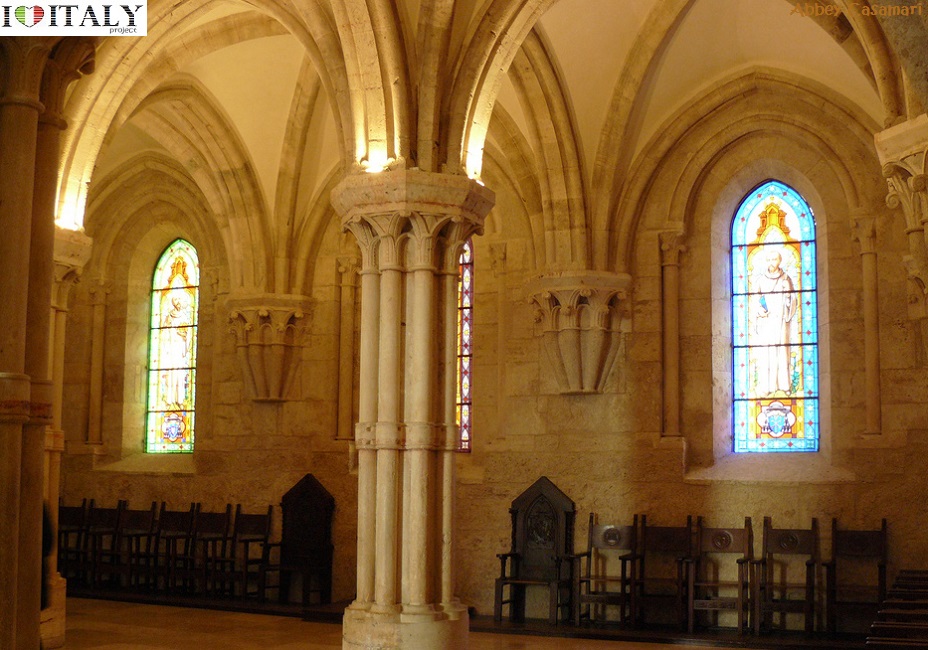  The Abbey of Saint Galgano was a Cistercian Monastery found in the valley of the river Merse between the towns of Chiusdino and Monticiano, in the province of Siena, region of Tuscany.
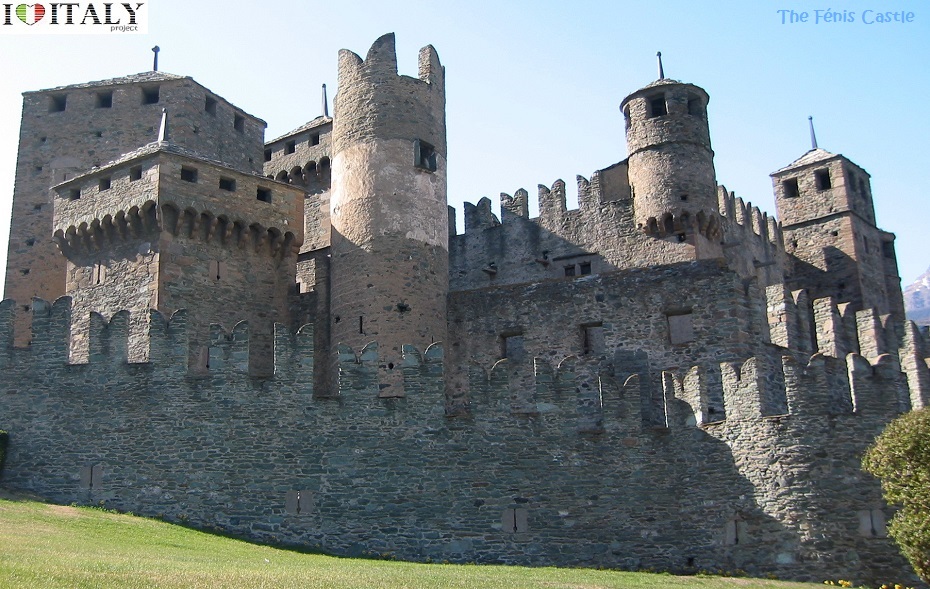
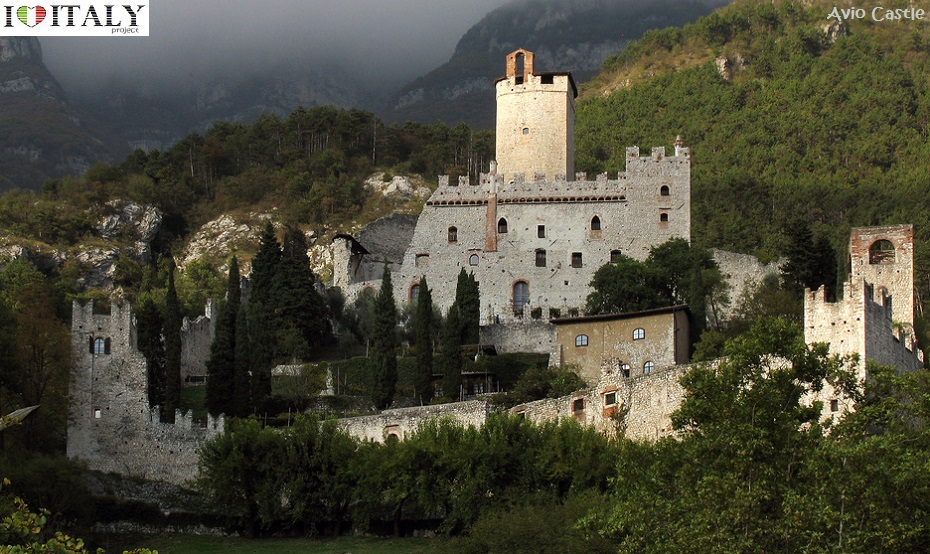
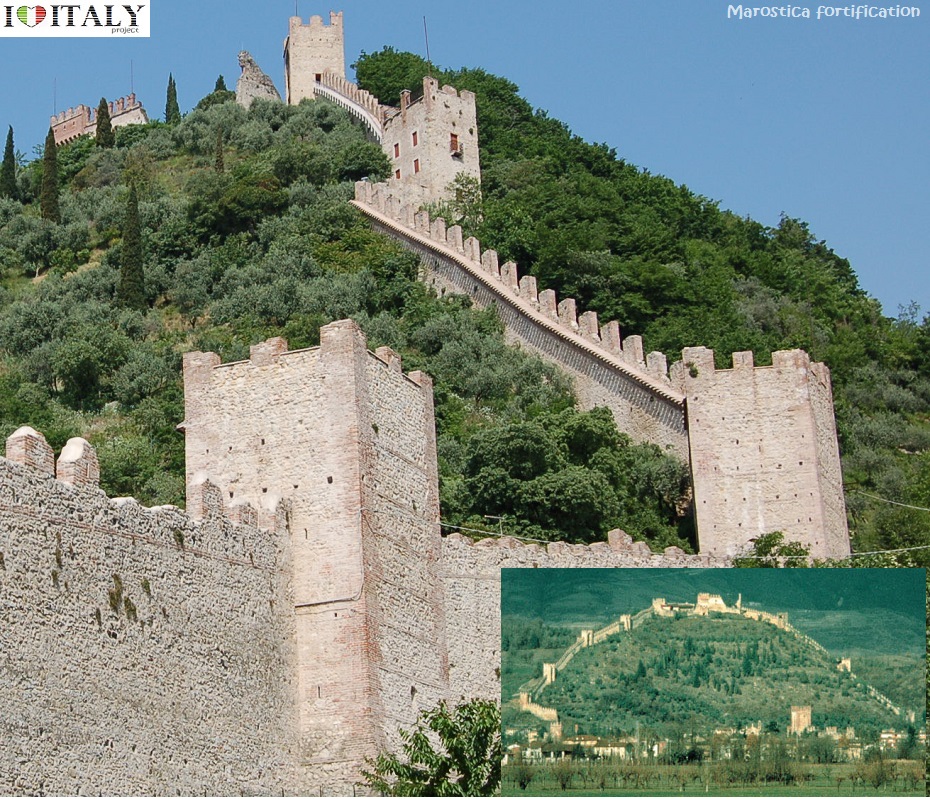
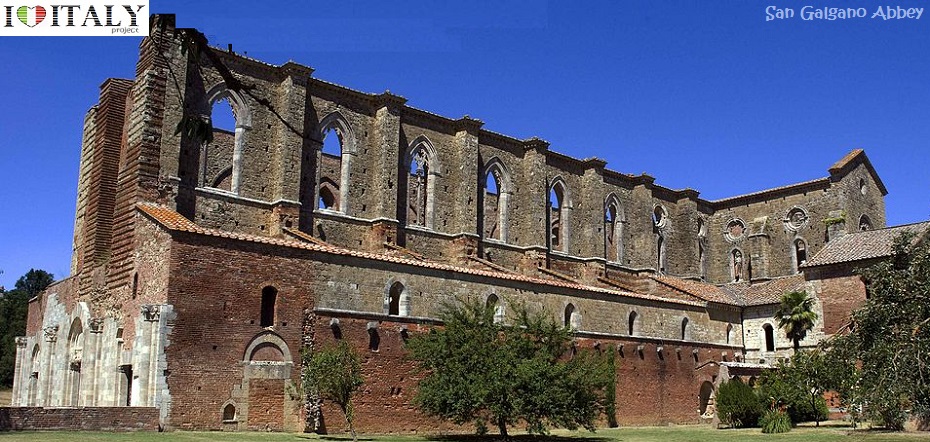 Presently, the roofless walls of the Gothic style 13th-century Abbey church still stand as majestic ruins in the countryside.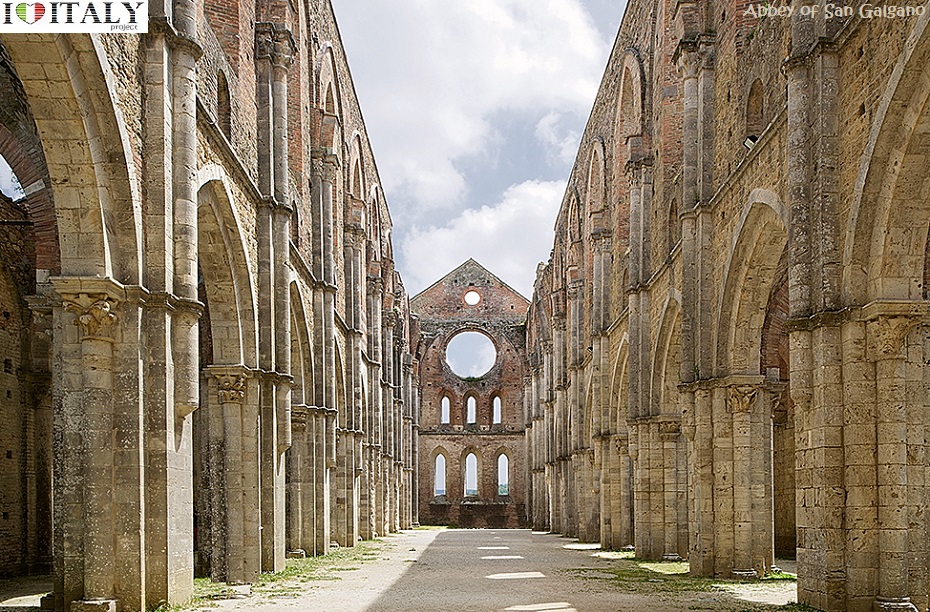   Fortifications, in all their various forms, are perhaps the most typical expression of secular architecture in the Gothic age. Castles (Fénis in Val d'Aosta, Avio in Trentino) and town fortifications (Marostica in Veneto, Monteriggioni in Tuscany) including towers and battlemented walls with moats and drawbridges.
The Fénis Castle is one of the major tourist attractions in the Valle d'Aosta. Known for its spectacular architecture, with double crenelated walls enclosing the central building and the many towers.
 The Castle of Sabbionara (also Castle of Avio) is mentioned for the first time in a 1053 document as Castellum Ava. The castle features three lines of walls, with five towers. Among the latter, the so-called Torre della Picadora was the place where executions (through hanging) were carried on.
 The fortification of Marostica ( Veneto Region) includes the two castles, the Upper and Lower, joined by a 1800 meters long wall.
 Monteriggioni is a comune in the province of Siena (Tuscany region). The circular defensive were built between 1213 and 1219. There are 14 towers and two portals or gates. One gate, the Porta Fiorentina opens toward Florence to the north, and the other, the Porta Romana, faces Rome to the south.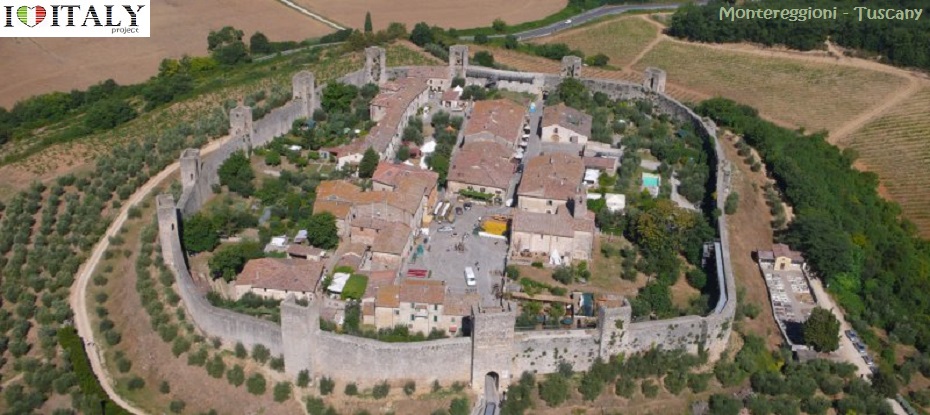  The castles built in the south by Frederick II of Swabia (Castel del Monte, castle of Oria) and those of the Visconti in Lombardy are particularly beautiful. Throughout the country, but especially in the centre and the south, there are fortified towns which have become a feature of the Italian landscape.
Equally distinctive are the medieval town centres, clearly marked out from areas of subsequent expansion. The 13th - century Castel del Monte is located near Andria, in the Apulia region. It was constructed during the 1240s by the Emperor Frederick II. The site is protected as a World Heritage Site. The octagonal plan is unusual in castle design. One theory is that the octagon is an intermediate symbol between a square (representing the earth) and a circle (representing the sky). Frederick II may have been inspired to build to this shape by either the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem, which he had seen during the Sixth Crusade, or by the Palace Chapel of Aachen Cathedral.
 Castle Oria (in the province of Brindisi - Apulia) occupies the hill of Vaglio, the highest part of the city, an area inhabited since remote times. The caste is listed as National Monument.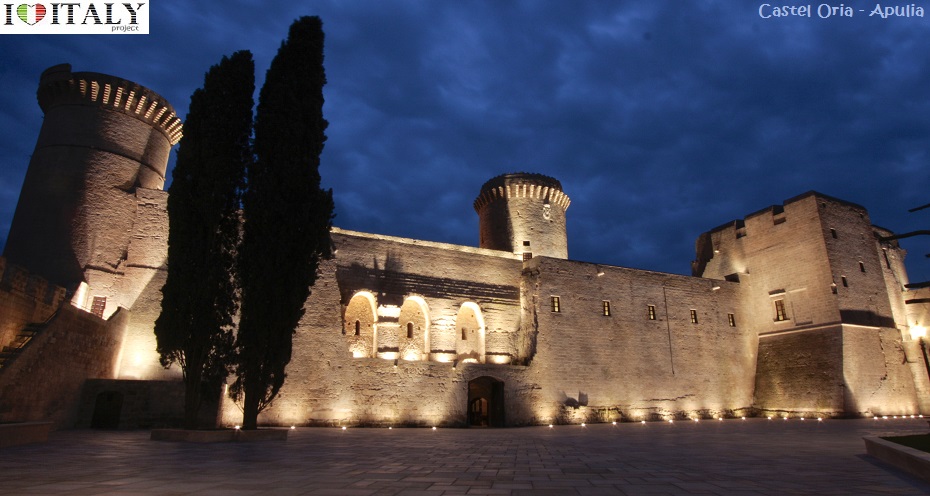  Il Castello Visconti, is to be found in Somma Lombardo , in the province of Varese, Lombardy. First mention of the castle can be traced back to a will dated June 22 , 1251. It was originally built as a fortress .
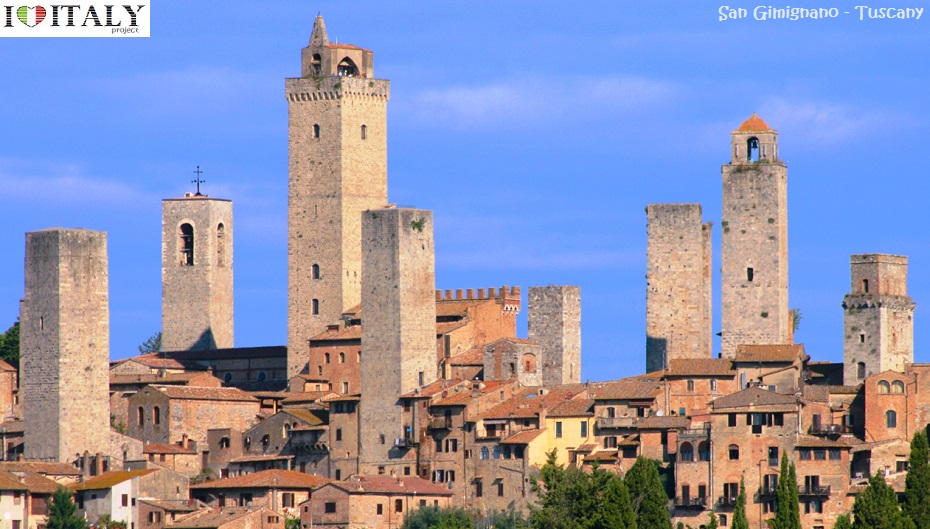
 Civil architecture also developed in cities through the building of house-towers (San Gimignano in Tuscany), markets, loggias, hospitals and above all the seats of municipal power (the town halls in Siena, Orvieto, Viterbo) or aristocratic power (Palazzo Ducale in Mantua) often looking like fortresses.
The "Historic Centre of San Gimignano", is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a classic example of both Romanesque and Gothic architecture. The medieval town is located in the province of Siena. Also known as the "Town of Fine Towers".
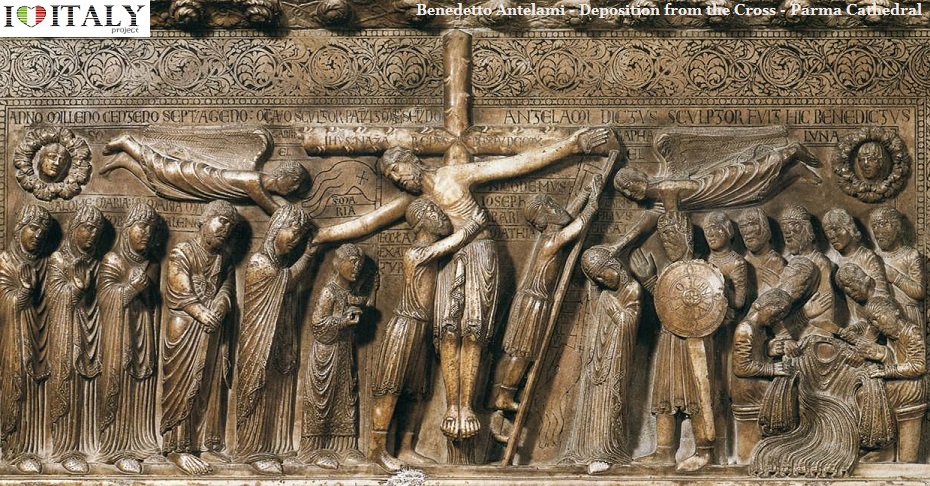
  The sculptures of Benedetto Antelami (Parma cathedral and baptistery) demonstrate the transition from Romanesque to Gothic. Deposition from the Cross. Here, in addition to the Provençal element, can be seen both classical and Byzantine influence.
 The works of Nicola Pisano (Pulpits of Siena Cathedral and Pisa Baptistery, Fountain in Perugia) and the Monument to Charles of d'Anjou by Arnolfo di Cambio in Campidoglio are classical inspiration. Pisano is sometimes considered to be the founder of modern sculpture.
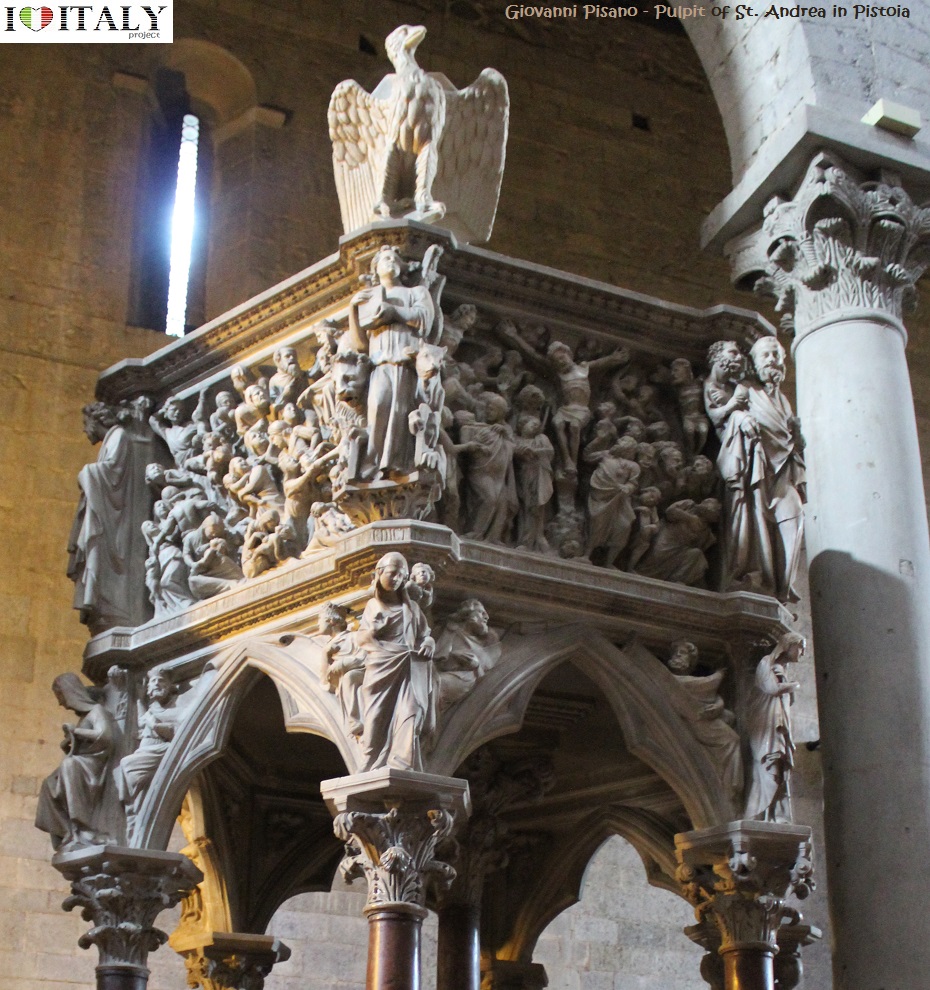
The Pisa Baptistry is an example of the transition from the Romanesque style to the Gothic style: the Baptistry is constructed of marble, plentiful and often used in Italian architecture.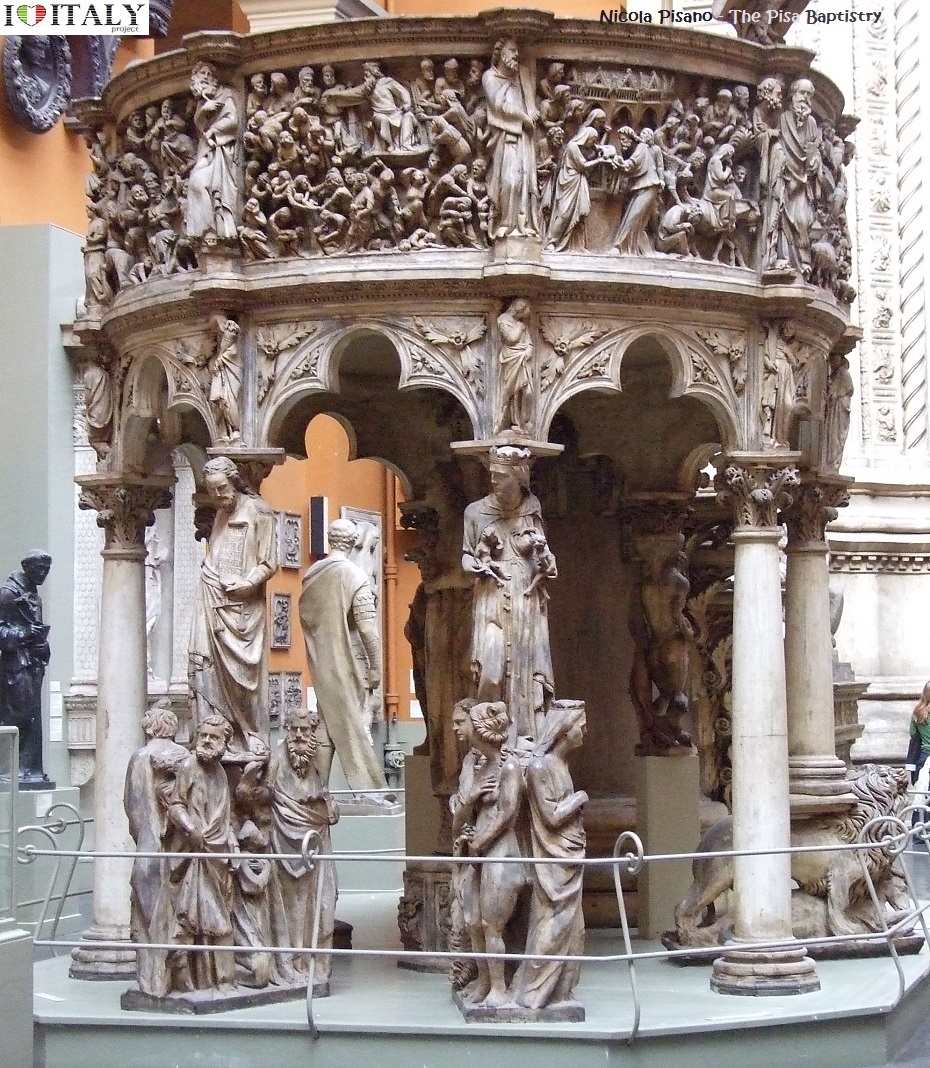  The Pulpits of St. Andrea in Pistoia and Pisa Cathedral also Giovanni Pisano reveal a linear taste close to French Gothic.
 Nino Pisano collaborated with his father, Andrea Pisano in many sculptures for the churches of San Zanipolo at Venice and in Santa Caterina at Pisa, and provided some panels for the bell tower of Santa Maria del Fiore. Nino succeeded his father in the works of the Orvieto Cathedral in 1349.
Some of his own works include the Madonna with Child in Santa Maria Novella, Florence, a Saint Bishop in the Cathedral of Oristano and a Monument to Bishop Scherlatti now in the Museum of Pisa Cathedral. His other attributed works include a Madonna of the Rose in Santa Maria della Spina, a Madonna with Child in Basilica of Maria S.S. Annunciata in Trapani and a Madonna del Latte in the Museum of St. Matthew, both in Pisa. An Annunciation, once in Santa Caterina, is now in the National Gallery of Art in Washington, D.C.   The fresco was triumphant in painting throughout the 14th century. The overtaking of the Byzantine tradition began in Assisi with the work of Cimabue, who increased spiritual tension by humanizing his figures, as in the Crucifix of Santa Croce in Florence. The badly damaged distemper on wood painting is one of three surviving crucifixes attributed to him. Representations of the Virgin and John the Evangelist flank christ in small rectangular panels at either end of his outstretched arms.
 The innovation became more pronounced in Rome with Pietro Cavallini (Last Judgment, Santa Cecilia) and then total with Giotto.  In the frescoes of the basilica of St. Francesco in Assisi, the Scrovegni chapel in Padua and in Santa Croce in Florence, Giotto developed a pictorial language rich in human and naturalistic elements which influenced all the painters of the time.
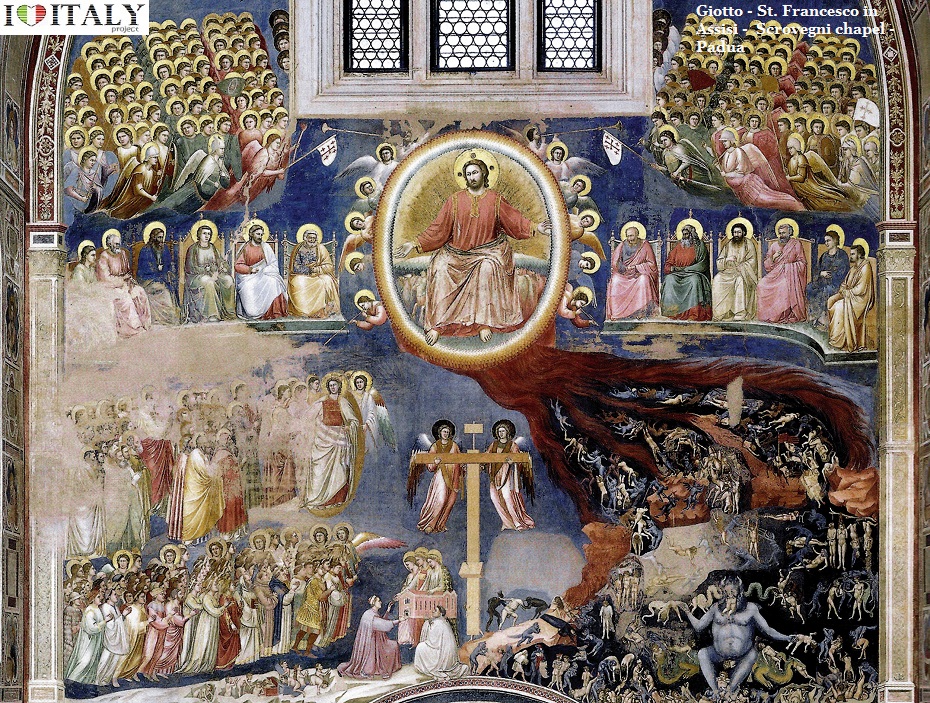 During the 14th century Siena witnessed the flourishing of the talent of Simeone Martini (Guidoriccio da Fogliano, Palazzo Pubblico). He was a major figure of early Italian painting and greatly influenced the development of the International Gothic style. Very little documentation of Simone's life survives, and many attributions are debated by art historians. It is suggested that Simone was a pupil of Giotto di Bondone, with whom he went to Rome to paint at the Old St. Peter's Basilica.
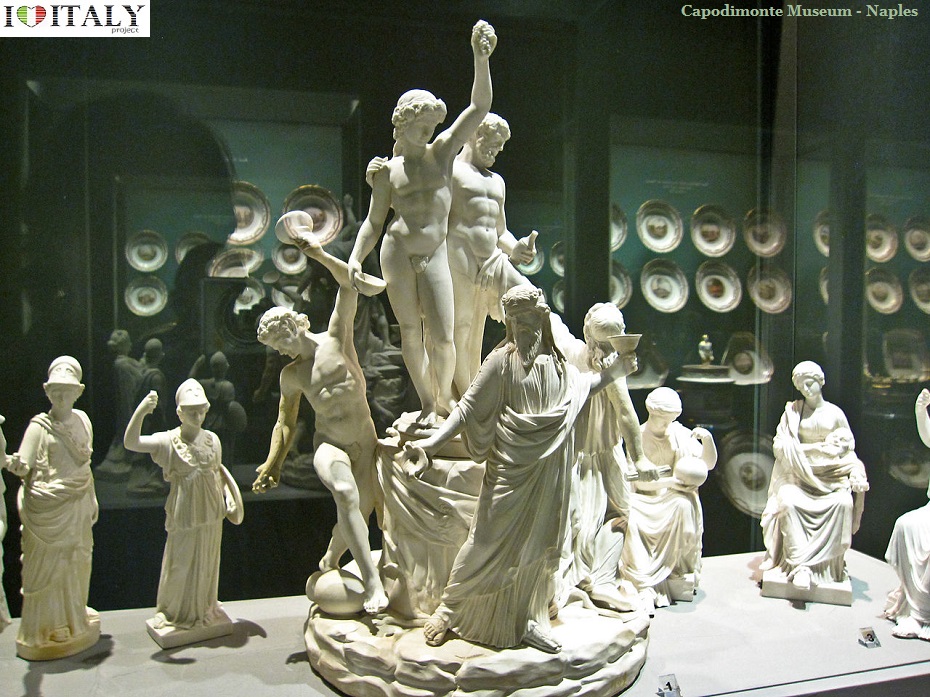
 Ambrogio Lorenzetti - The Allegory of Good and Bad Government is a series of frescoes from around February 26, 1338 to May 29, 1339. The paintings are located in the Sala dei Nove (Salon of Nine or Council Room) in Siena's town hall. The series consists of six different scenes: Allegory of Good Government, Allegory of Bad Government, Effects of Bad Government in the City, Effects of Good Government in the City and Effects of Good Government in the Country (the titles are all modern conveniences).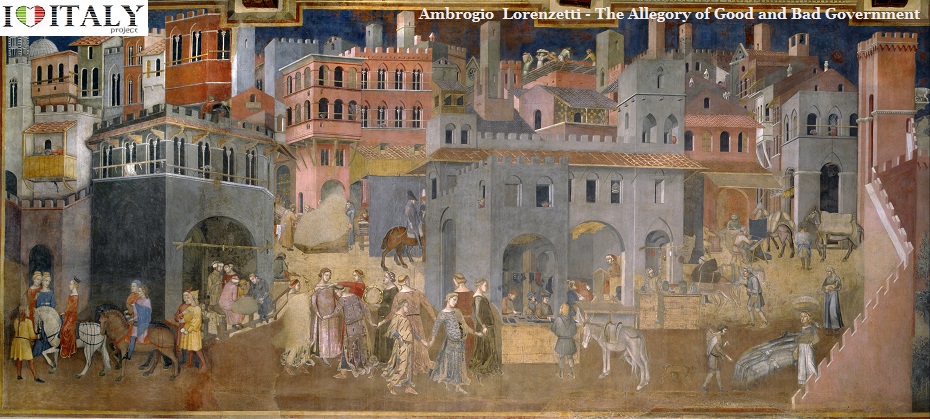   Minor Arts - In the Gothic period the art of stained glass windows also developed in Italy but without achieving the splendor of northern Europe because in Italian churches frescoed walls were usually more important than windows. Good examples are found in the cathedral of Orvieto and Milan . 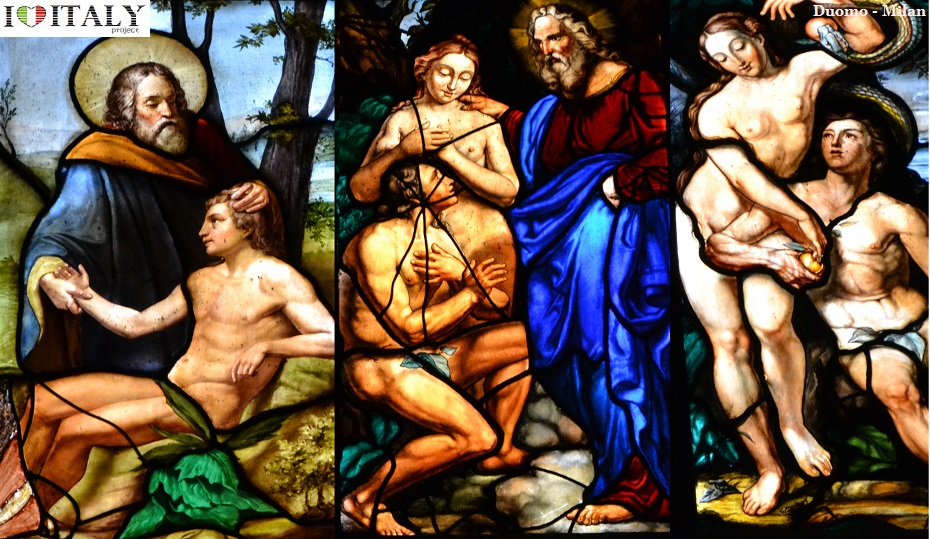 The arts of ivory engraving (Embriachi tryptych, Certosa di Pavia, image below with) jewellery and drawing (Bergamo, Biblioteca Civica) also flourished in the 14th century.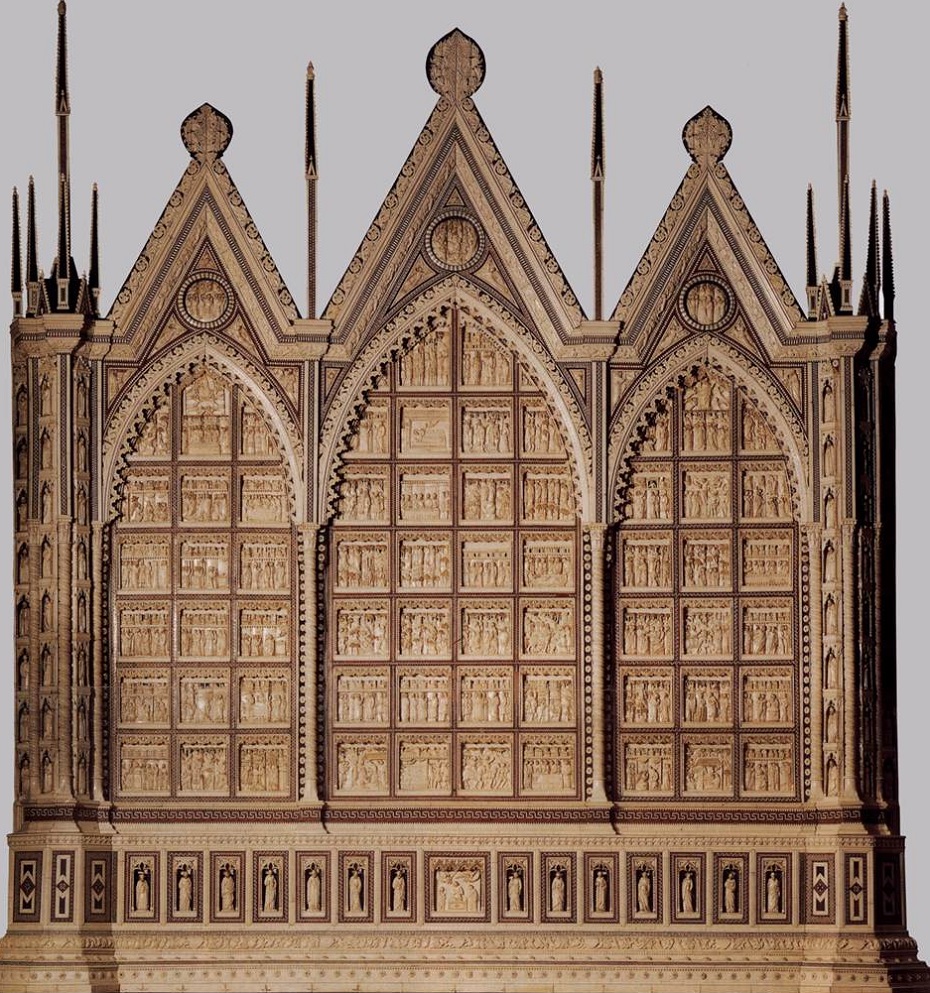  Details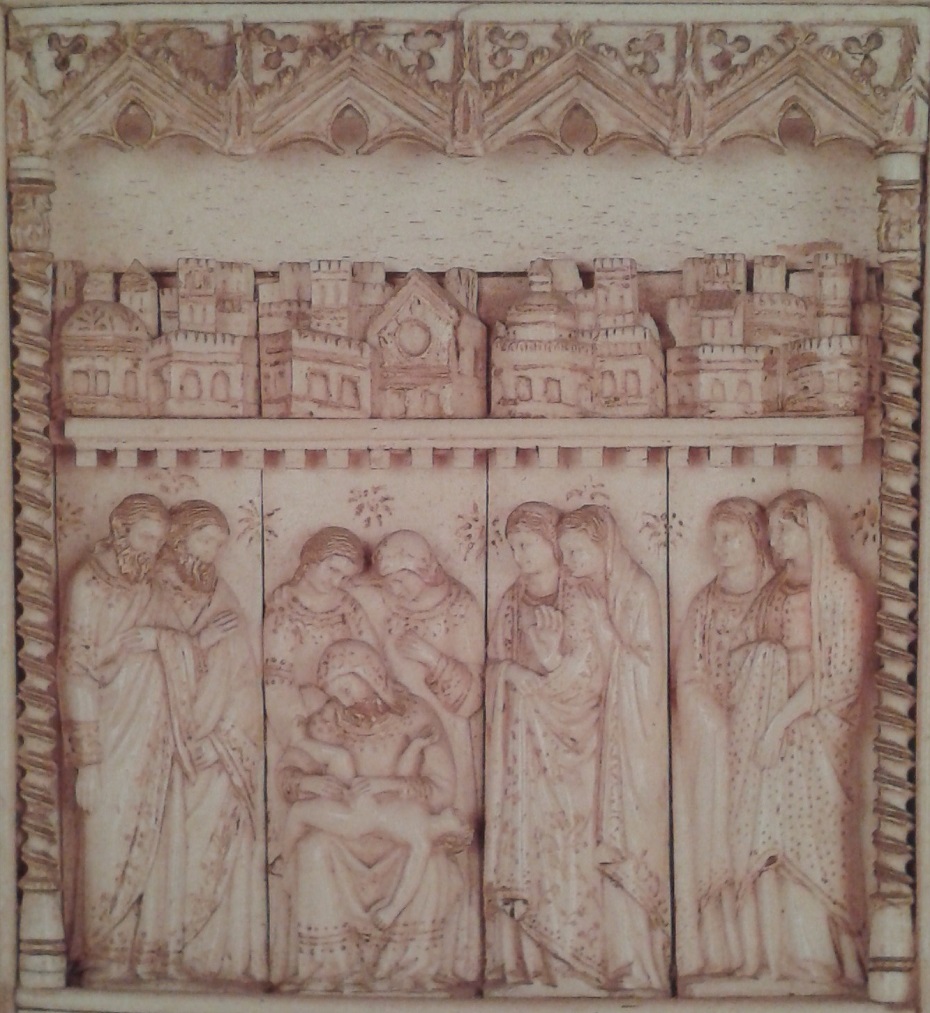 
Where to stay
Your tour guide
Shopping
CERCASI ALLOGGI DI QUALITA'
B & B Farm House - Masserie / Agriturismo Hotel Resort Room for rent - Affittacamere Apartment for rent - Appartamenti Houses for rent - Case in affitto MAX : CINQUE ESERCIZI PER OGNI CATEGORIA x REGIONE Are You a tourist guide?  Do you organize tours to northern & southern Italy? If the thematic is based on culture, history and outdoor activities, we would love to talk to you. Drop us a line. MADE IN ITALY PRODOTTI LOCALI SOUVENIRS Contattateci tramite il modulo soprastante.  Se sei in grado di promuovere il tuo territorio con le sue produzioni enogastronomiche, le sue strutture ricettive e le sue bellezze storiche e artistiche, Made in South Italy può essere la piattaforma ideale per raccontare e rappresentare i "mille" territori italiani , ben consapevole che per farlo meglio e in modo completo ha bisogno della collaborazione di chi vive in quei luoghi, li conosce dall’interno e li sa rappresentare. Interessati? Se sei in grado di promuovere il tuo territorio con le sue produzioni enogastronomiche, le sue strutture ricettive e le sue bellezze storiche e artistiche, Made in South Italy può essere la piattaforma ideale per raccontare e rappresentare i "mille" territori italiani , ben consapevole che per farlo meglio e in modo completo ha bisogno della collaborazione di chi vive in quei luoghi, li conosce dall’interno e li sa rappresentare. Interessati?La vetrina ideale per promuovere i vostri prodotti e servizi sul mercato Nord Americano ma che potrebbe essere un punto di visibilità anche nei vari mercati internazionali.
 Paesi di provenienza dei visitatori in ordine numerico Stati Uniti - Canada - Italia - Gran Bretagna - Australia - China - Germania - Francia - Nuova Zelanda - Olanda Coloro interessati ad inserire la loro attivita'/azienda/ nel sito
|
|||||||||||||||||